实践-收集K8S日志
用 Filebeat 做 k8s 的日志采集,部署方式是采用DaemonSet的方式,采集时按照 k8s 集群的namespace进行分类。
K8S日志文件说明
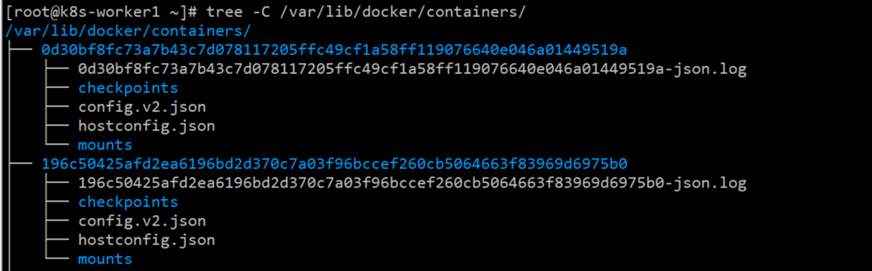
一般情况下,容器中的日志在输出到标准输出(stdout)时,会以*-json.log的命名方式保存在/var/lib/docker/containers目录中,当然如果修改了docker的数据目录,那就是在修改后的数据目录中了,例如:
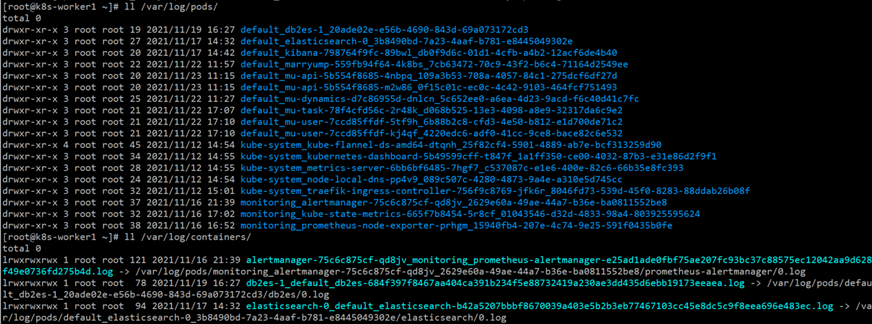
这里能看到,有这么个文件:/var/lib/docker/containers/container id/*-json.log,然后 k8s 默认会在/var/log/containers和/var/log/pods目录中会生成这些日志文件的软链接,如下所示:
然后,会看到这个目录下存在了此宿主机上的所有容器日志,文件的命名方式为:
[podName]_[nameSpace]_[depoymentName]-[containerId].log
上面这个是deployment的命名方式,其他的会有些不同,例如:DaemonSet,StatefulSet等,不过所有的都有一个共同点,就是
*_[nameSpace]_*.log
到这里,知道这个特性,就可以往下来看Filebeat的部署和配置了。
Filebeat部署
部署采用DaemonSet方式进行,参照官方文档部署即可:
配置文件:
vim filebeat-config.yml
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: filebeat-config
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
data:
filebeat.yml: |-
filebeat.inputs:
- type: container
enabled: true
paths:
- /var/log/containers/*-ingress*.log
fields:
event.dataset: k8s.ingress
fields_under_root: true
processors:
- add_kubernetes_metadata:
host: ${NODE_NAME}
matchers:
- logs_path:
logs_path: "/var/log/containers/"
filebeat.autodiscover:
providers:
- type: kubernetes
templates:
- condition:
equals:
kubernetes.namespace: default
config:
- type: container
paths:
- "/var/log/containers/*-${data.kubernetes.container.id}.log"
fields:
event.dataset: k8s.apps
fields_under_root: true
filebeat.config.modules:
path: ${path.config}/modules.d/*.yml
reload.enabled: false
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 1
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["192.168.220.31:9200","192.168.220.32:9200","192.168.220.33:9200"]
indices:
- index: "filebeat-%{[event.dataset]}-%{+yyyy.MM}"
processors:
- add_cloud_metadata:
- add_host_metadata:
- drop_fields:
fields:
- host
- ecs
- log
- input
- kubernetes
kubectl create -f filebeat-config.yml
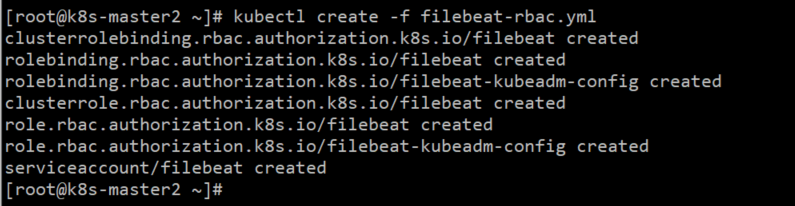
RBAC权限:
vim filebeat-rbac.yml
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: filebeat
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: filebeat
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: filebeat
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: filebeat-kubeadm-config
namespace: kube-system
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: filebeat-kubeadm-config
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: filebeat
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # "" indicates the core API group
resources:
- namespaces
- pods
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- watch
- list
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources:
- replicasets
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: filebeat
# should be the namespace where filebeat is running
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
rules:
- apiGroups:
- coordination.k8s.io
resources:
- leases
verbs: ["get", "create", "update"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: filebeat-kubeadm-config
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources:
- configmaps
resourceNames:
- kubeadm-config
verbs: ["get"]
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
kubectl create -f filebeat-rbac.yml
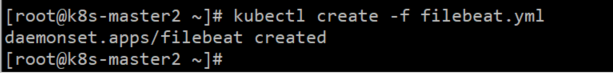
Filebeat创建:
vim filebeat.yml
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: filebeat
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: filebeat
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: filebeat
spec:
serviceAccountName: filebeat
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
hostNetwork: true
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirstWithHostNet
containers:
- name: filebeat
image: docker.elastic.co/beats/filebeat:7.16.2
args: [
"-c", "/etc/filebeat.yml",
"-e",
]
env:
- name: NODE_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: spec.nodeName
securityContext:
runAsUser: 0
# If using Red Hat OpenShift uncomment this:
#privileged: true
resources:
limits:
memory: 200Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 100Mi
volumeMounts:
- name: config
mountPath: /etc/filebeat.yml
readOnly: true
subPath: filebeat.yml
- name: data
mountPath: /usr/share/filebeat/data
- name: varlibdockercontainers
mountPath: /var/lib/docker/containers
readOnly: true
- name: varlog
mountPath: /var/log
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: config
configMap:
defaultMode: 0640
name: filebeat-config
- name: varlibdockercontainers
hostPath:
path: /var/lib/docker/containers
- name: varlog
hostPath:
path: /var/log
# data folder stores a registry of read status for all files, so we don't send everything again on a Filebeat pod restart
- name: data
hostPath:
# When filebeat runs as non-root user, this directory needs to be writable by group (g+w).
path: /var/lib/filebeat-data
type: DirectoryOrCreate
kubectl create -f filebeat.yml
Tips:拉取镜像可能会超时,注意预先处理。
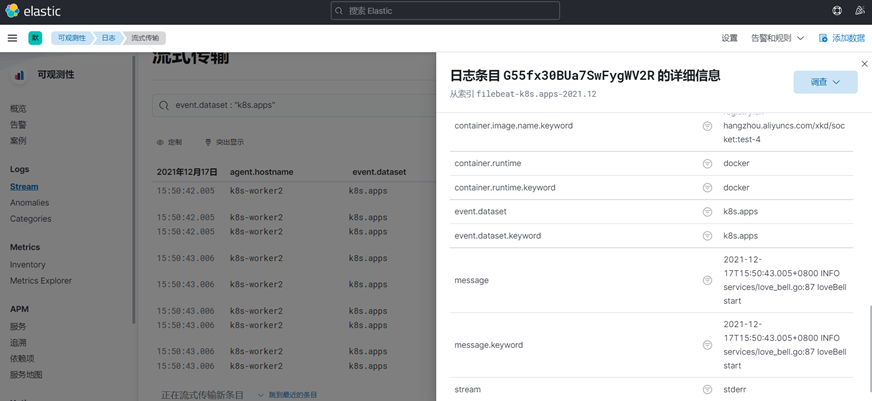
查看
部署完后即会按配置运行,查看ES中收集到的信息:
索引:
日志: